All About Boiled Ham: A Classic and Versatile Ingredient
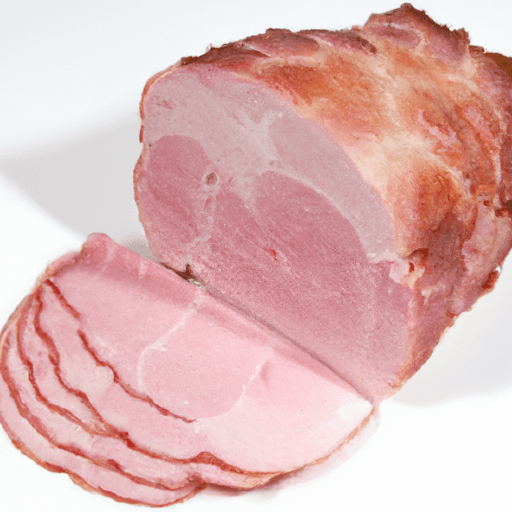
Boiled ham is a beloved and versatile ingredient that has been enjoyed for generations. With its tender and succulent texture, distinct flavor, and rich history, boiled ham holds a special place in the kitchen. In this blog post, we will delve into the delightful world of boiled ham, exploring its taste, common uses in cooking, nutritional value, and uncover some interesting history and facts along the way.
The Taste of Boiled Ham: A Perfect Balance of Saltiness and Sweetness
Boiled ham offers a delectable taste that is both salty and subtly sweet, making it a popular choice for a variety of culinary creations. The saltiness is derived from the curing process the ham undergoes before boiling, which helps preserve it and infuse it with flavor. This flavor profile combines harmoniously with a touch of natural sweetness, resulting in a well-balanced, irresistible taste.
Common Uses and Culinary Versatility
Boiled ham is highly versatile, making it a staple in countless recipes. Here are some of the most common uses that highlight its culinary flexibility:
- Sandwiches: Thinly sliced boiled ham is a classic choice for sandwiches, adding a savory and satisfying element to any combination of bread, cheese, and condiments.
- Pasta Dishes: Diced or shredded boiled ham can elevate pasta dishes, such as carbonara or creamy Alfredo, by providing a burst of flavor and texture.
- Quiches and Frittatas: Incorporating boiled ham into quiches or frittatas adds substance and depth, creating a hearty and nourishing meal.
- Soup and Stew: Chunks of boiled ham serve as a delicious addition to soups and stews, infusing them with a rich, meaty essence.
- Salads: From chef salads to Caesar salads, chopped boiled ham contributes a savory note and turns a simple salad into a satisfying main course.
Nutritional Value: A Wholesome Choice
Apart from its mouthwatering taste, boiled ham also offers several nutritional benefits. It is an excellent source of protein, essential for muscle growth and repair. Additionally, it contains important vitamins and minerals, including iron, vitamin B12, and zinc. However, it’s worth noting that boiled ham tends to be higher in sodium, so moderation is key, especially for individuals on a low-sodium diet.
History and Fun Facts
Boiled ham has a rich history dating back centuries. Its roots can be traced to the ancient Roman process of salting and smoking pork. Over time, this preservation technique evolved, leading to the creation of the boiled ham we know and love today.
Interestingly, boiled ham became especially popular in Europe during the Renaissance period. A delicacy fit for nobility, it graced the tables of kings and queens, further contributing to its enduring legacy.
In the United States, boiled ham gained prominence in the early 20th century when it became a favored protein choice for school lunches. Its affordability, ease of preparation, and crowd-pleasing taste made it a reliable option in cafeterias across the nation.
Conclusion
Boiled ham is undoubtedly a cherished ingredient that brings joy to many kitchen endeavors. Its harmonious blend of salty and sweet flavors, culinary versatility, and wholesome nutritional value make it a top contender in countless recipes. Whether it’s a mouthwatering sandwich or a comforting bowl of soup, boiled ham has the power to transform ordinary dishes into extraordinary culinary experiences. So, next time you’re seeking a flavorful and trustworthy ingredient, look no further than the timeless appeal of boiled ham.
Boiled Ham
Origin: The origins of boiled ham can be traced back to ancient times when civilizations began the practice of preserving meat through various cooking methods. Boiling, as a technique, was commonly used for preserving and cooking ham in many different cultures.
Common Uses: Boiled ham is typically used as a standalone dish or as an ingredient in various recipes. It is often served as the main course in traditional holiday meals. Boiled ham can also be sliced and used in sandwiches, salads, and soups.
Nutritional Benefits: Boiled ham is a good source of protein, essential vitamins, and minerals. It is relatively low in fat, particularly if any visible fat is trimmed before cooking. However, due to the curing process, boiled ham tends to be high in sodium, so it should be consumed in moderation by individuals concerned about their sodium intake.
Unique Properties and Historical Significance: Boiled ham is distinctive for its tender and moist texture, resulting from the cooking process. The ham is simmered in flavored liquid, which helps to infuse it with added taste. Throughout history, boiled ham has been a popular choice for special feasts, holidays, and celebratory occasions. It has become a staple in many cultures and is often associated with festive meals.



Use the share button below if you liked it.
It makes me smile, when I see it.